config controller in action
In August 2021, Anthos Config Management (ACM) got a new feature called Config Controller, a hosted service to provision and orchestrate Google Cloud resources.
Config Controller offers an API endpoint that can provision, actuate, and orchestrate Google Cloud resources the same way it manages Kubernetes resources. You don’t have to install or manage the components—or be an expert in Kubernetes resource management or GitOps—because Google Cloud will manage them for you.
Config Controller is a bundle of the 3 following components:
- Config Sync - to create what you need from a single source of truth
- Policy Controller - to enforce the security and compliance of your resource configurations
- Config Connector - to create GCP resources by using the Kubernetes Resource Model (KRM)
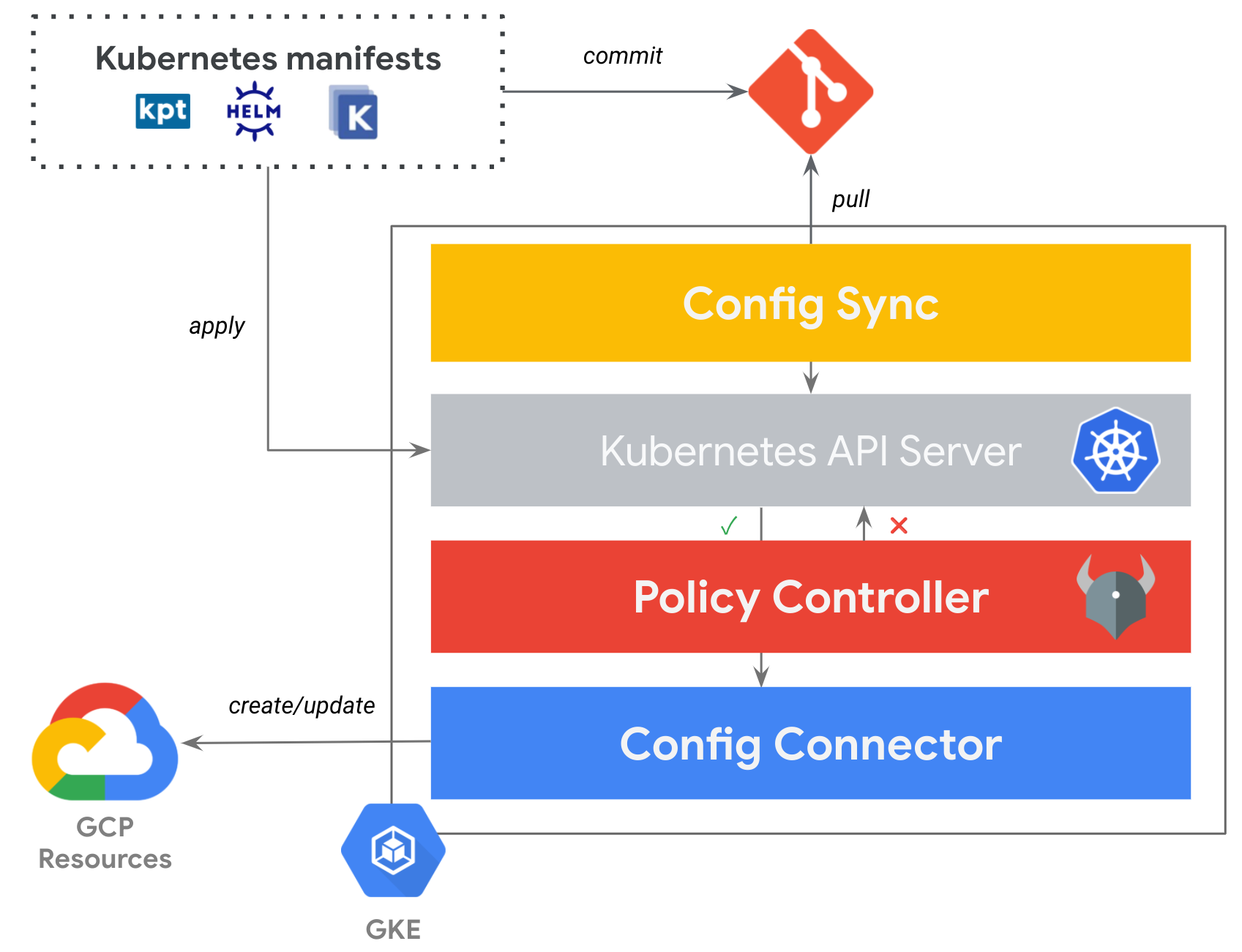
Now, let’s see this in action!
Note: for now, we will just illustrate Config Connector and Policy Controller, not yet Config Sync, but if you read until the end, you will find that pointer to my other blog article covering this GitOps story as a part 2 of this one.
Here is what we are going to accomplish:
- Set up Config Controller
- Set up Policies
- Set up Tenant project
- Set up ConfigConnectorContext for Tenant project
- Create GCP resources in Tenant project
- Further considerations
Here is what we are going to illustrate throughout this blog article:
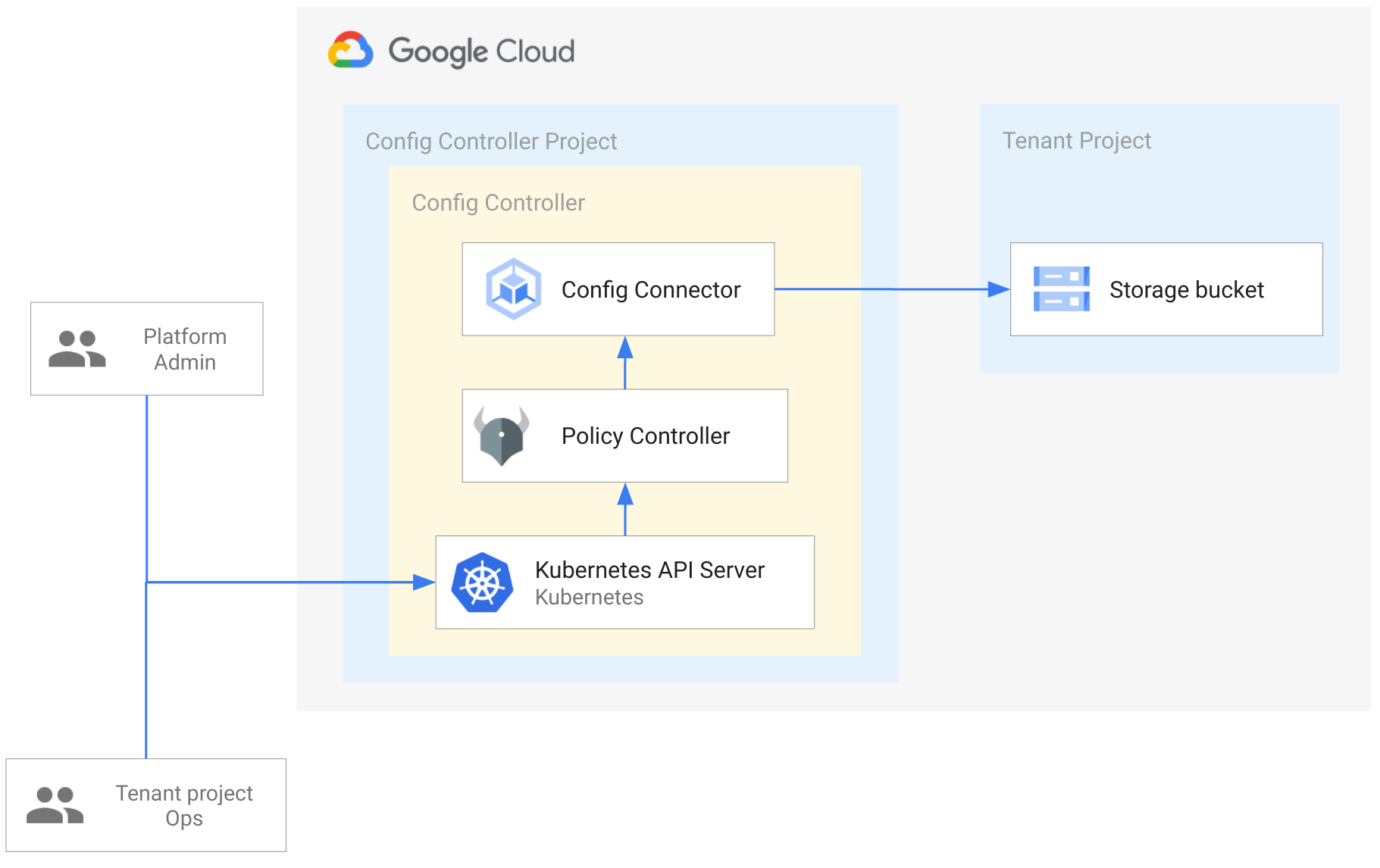
Set up Config Controller
As Platform Admin, I want to create a Config Controller instance to provide a centralized place as a Kubernetes Server API endpoint in order to provision any GCP resources for my entire company.
Enable the required API:
CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PROJECT_ID=FIXME
gcloud config set project $CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PROJECT_ID
gcloud services enable krmapihosting.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com
Create a Config Controller instance:
CONFIG_CONTROLLER_NAME=FIXME
CONFIG_CONTROLLER_LOCATION=us-east1 # or us-central1 are supported for now
LOCAL_IP_ADDRESS=$(curl ifconfig.co) # Change this if needed to properly get your local IP address
gcloud anthos config controller create $CONFIG_CONTROLLER_NAME \
--location=$CONFIG_CONTROLLER_LOCATION \
--man-block $LOCAL_IP_ADDRESS/32
Note: by default the Master Authorized Network (--man-block) is configured with 0.0.0.0/0, we just limited the access to the Kubernetes API Server to our local IP address to add more security.
From here, it will take 15+ min to provision the Config Controller instance. Once provisioned you could check its status:
gcloud anthos config controller list \
--location=$CONFIG_CONTROLLER_LOCATION
gcloud anthos config controller describe $CONFIG_CONTROLLER_NAME \
--location=$CONFIG_CONTROLLER_LOCATION
Set up Policies
As Platform Admin, I want to set up policies in order to control what’s deployed and have in place common best practices and compliances accross my company.
You could create your own ConstraintTemplate, but you could also reuse the ConstraintTemplates already installed by default for you (see the output of kubectl get constrainttemplates).
Let’s for example make sure that any Namespace has a label owner:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: constraints.gatekeeper.sh/v1beta1
kind: K8sRequiredLabels
metadata:
name: ns-must-have-owner
spec:
match:
kinds:
- apiGroups: [""]
kinds: ["Namespace"]
parameters:
labels:
- key: "owner"
EOF
Another example could be to only allow a specific list of locations where the GCP Storage buckets could be provisioned:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: constraints.gatekeeper.sh/v1beta1
kind: GCPStorageLocationConstraintV1
metadata:
name: gcp-storage-location-restriction
spec:
match:
kinds:
- apiGroups:
- storage.cnrm.cloud.google.com
kinds:
- StorageBucket
parameters:
locations:
- us-east1
EOF
Set up Tenant project
As Platform Admin, I want to set up a dedicated namespace and GCP project to onboard a specific project for a specific team.
By default, you could deploy any GCP resources in the GCP project where your Config Controller is deployed. For doing so, you need to grant the Config Controller’s service account (kubectl get ConfigConnectorContext -n config-control -o jsonpath='{.items[0].spec.googleServiceAccount}') the proper GCP roles and deploy your Kubernetes manifests in the config-control namespace.
But here what we want to do is to create a dedicated namespace and project for each team/project where associated GCP resources will be deployed in. We are leveraging the namespaced mode of Config Connector, and we will configure it in order to manage resources in namespaces.
First, we need to grant the Config Controller’s service account the proper roles. In our case we want to create different projects and assign them the right billing account:
gcloud services enable cloudbilling.googleapis.com --project ${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PROJECT_ID}
CONFIG_CONTROLLER_SA="$(kubectl get ConfigConnectorContext -n config-control -o jsonpath='{.items[0].spec.googleServiceAccount}')"
ORG_ID=FIXME
BILLING_ACCOUNT_ID=FIXME
gcloud organizations add-iam-policy-binding ${ORG_ID} \
--member="serviceAccount:${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_SA}" \
--role='roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator'
gcloud organizations add-iam-policy-binding ${ORG_ID} \
--member="serviceAccount:${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_SA}" \
--role='roles/billing.projectManager'
gcloud beta billing accounts add-iam-policy-binding ${BILLING_ACCOUNT_ID} \
--member="serviceAccount:${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_SA}" \
--role='roles/billing.user'
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PROJECT_ID} \
--member="serviceAccount:${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_SA}" \
--role='roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageConsumer'
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PROJECT_ID} \
--member="serviceAccount:${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_SA}" \
--role='roles/iam.serviceAccountAdmin'
Then we need to create the tenant project in the config-control namespace:
RANDOM_SUFFIX=$(shuf -i 100-999 -n 1)
TENANT_PROJECT_ID=tenant-$RANDOM_SUFFIX # should be unique
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: resourcemanager.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1
kind: Project
metadata:
annotations:
cnrm.cloud.google.com/auto-create-network: "false"
name: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
namespace: config-control
spec:
name: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
billingAccountRef:
external: "${BILLING_ACCOUNT_ID}"
organizationRef:
external: "${ORG_ID}"
resourceID: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
EOF
Check that the project is successfully created: kubectl wait --for=condition=READY project $TENANT_PROJECT_ID -n config-control.
Note: The tenant project was created at the organization level, but it’s also possible to create this tenant project in a folder, see reference here.
Now what we need to do is to create a dedicated GCP service account for this project, still in the config-control namespace:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: iam.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1
kind: IAMServiceAccount
metadata:
name: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
namespace: config-control
spec:
displayName: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
---
apiVersion: iam.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1
kind: IAMPartialPolicy
metadata:
name: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}-sa-workload-identity-binding
namespace: config-control
spec:
resourceRef:
name: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
apiVersion: iam.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1
kind: IAMServiceAccount
bindings:
- role: roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser
members:
- member: serviceAccount:${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PROJECT_ID}.svc.id.goog[cnrm-system/cnrm-controller-manager-${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}]
EOF
Set up ConfigConnectorContext for Tenant project
The Tenant project namespace needs its own ConfigConnectorContext resource in order to invoke its dedicated GCP service account:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
annotations:
cnrm.cloud.google.com/project-id: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
labels:
owner: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
name: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
---
apiVersion: core.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1
kind: ConfigConnectorContext
metadata:
name: configconnectorcontext.core.cnrm.cloud.google.com
namespace: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
spec:
googleServiceAccount: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}@${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com
EOF
Create GCP resources in Tenant project
Before actually provisioning a GCP Storage Bucket, we need to grant the storage.admin role to the Tenant project’s service account via an IAMPolicyMember resource deployed in the config-control namespace (where this service account is):
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: iam.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1
kind: IAMPolicyMember
metadata:
name: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}-storage-admin
namespace: config-control
spec:
member: serviceAccount:${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}@${CONFIG_CONTROLLER_PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com
role: roles/storage.admin
resourceRef:
apiVersion: resourcemanager.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1
kind: Project
external: projects/${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
EOF
As Tenant project Ops, I want to deploy GCP resources in my Tenant project.
Now let’s provision the GCP Storage Bucket in the Tenant project’s namespace via a StorageBucket resource:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: storage.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1
kind: StorageBucket
metadata:
annotations:
cnrm.cloud.google.com/force-destroy: "false"
name: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
namespace: ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}
spec:
location: us-east1
uniformBucketLevelAccess: true
EOF
You could check that this GCP Storage bucket has been created successfully with kubectl get StorageBucket -n ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID} and gsutil ls -p ${TENANT_PROJECT_ID}.
Congrats! You made it! You have set up a platform with Config Controller to securely deploy GCP resources via a platform for your teams/projects.
Further considerations
So, that was part 1, are you ready for part 2 to see how to set up a GitOps approach with all of that thanks to Config Controller? If yes, check this out!
Hope you enjoyed that one, happy sailing! ;)